*注意* vyatta-2013-03-14.iso から IID を draft-ietf-softwire-map-04 の形式に変更しました。過去のバージョンとの互換性が無くなっておりますのでアップグレードする際は必ず全ての BR と CE を同時にアップグレードしてください。また、デフォルトの PSID offset も 4 から 6 に変更しました。こちらも同様に BR と CE で設定が統一されている必要がありますのでご注意下さい。(この経緯については http://www.ietf.org/mail-archive/web/softwires/current/msg05266.html をご確認下さい。)
NOTE: vyatta-2013-03-14.iso or later is implemented based on draft-ietf-softwire-map-04. When upgrading, you need to do that on all of BRs/CEs at once because of compatibility issues about IID and changing PSID offset from 4 to 6. Please read http://www.ietf.org/mail-archive/web/softwires/current/msg05266.html for detailed story.
| Name | Last modified | Size | Description | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Parent Directory | - | |||
| vyatta-op_999.dev_all.deb | 04-Mar-2020 11:00 | 132K | ||
| vyatta-op-2014-03-07.patch | 04-Mar-2020 11:00 | 1.5K | ||
| vyatta-cfg-system_999.dev_i386.deb | 04-Mar-2020 11:00 | 218K | ||
| vyatta-cfg-system-2014-03-07.patch | 04-Mar-2020 11:00 | 16K | ||
| vyatta-2014-03-07.iso | 04-Mar-2020 11:00 | 212M | ||
| old/ | 04-Mar-2020 11:00 | - | ||
| linux-vyatta-kbuild_999.dev_i386.deb | 04-Mar-2020 11:00 | 57M | ||
| linux-libc-dev_999.dev_i386.deb | 04-Mar-2020 11:00 | 1.2M | ||
| linux-image-2014-03-07.patch | 04-Mar-2020 11:00 | 179K | ||
| linux-image-3.3.8-1-586-vyatta_999.dev_i386.deb | 04-Mar-2020 11:00 | 21M | ||
| iproute_20120801-vyatta+2+pacifica1_i386.deb | 04-Mar-2020 11:00 | 665K | ||
| iproute-2014-03-07.patch | 04-Mar-2020 11:00 | 37K | ||
| img/ | 04-Mar-2020 11:00 | - | ||
| LICENSE | 04-Mar-2020 11:00 | 445 | ||
MAP の詳細は draft-ietf-softwire-map を参照のこと。
Please refer to draft-ietf-softwire-map for details of MAP protocol.
vyatta-YYYY-MM-DD.iso の最新版をダウンロードしてインストールしてください。
Download the latest version of vyatta-YYYY-MM-DD.iso, and then install it.
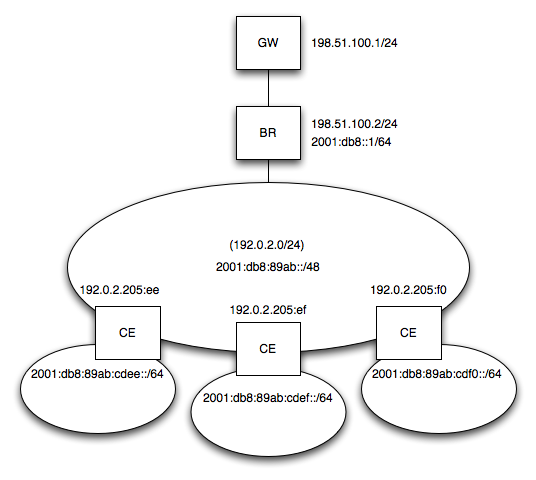
MAP-T として利用したいときは以下のように設定します。
If you configure ASAMAP for MAP-T, please set the following command.
# set interfaces map map0 default-forwarding-mode translation
MAP-E として利用したいときは以下のように設定します。
If you configure ASAMAP for MAP-E, please set the following command.
# set interfaces map map0 default-forwarding-mode encapsulation
default-forwarding-mode はすべての BR/CE で同じ設定がされている必要があります。
All BR/CE are required to have same default-forwarding-mode.
Mesh 構成としたい場合(CE 間の直接通信を許可したい場合)は CE で以下のように設定します。(この設定はデフォルトなので省略可能です。)
In the case of mesh topology in the MAP domain, please set the following on all CEs. This configuration is default setting.
# set interfaces map map0 default-forwarding-rule true
Hub & Spoke 構成としたい場合(CE 間の通信はかならず BR を経由させたい場合)は CE で以下のように設定します。
In the case of hub & spoke topology in the MAP domain, please set the following on all CEs.
# set interfaces map map0 default-forwarding-rule false
Mesh、 Hub & Spoke 共に BR 側は必ず default-forwarding-rule true にしてください。
Regarding BRs, please set "default-forwarding-rule true", regardless of topology type.
以下のように Mapping Rule 毎に forwarding-mode と forwarding-rule を個別に指定することもできます。ただし forwarding-mode はすべての BR/CE で同じように設定されている必要が有ります。
You can set the individual parameter of "forwarding-mode" and "forwarding-rule" according to each mapping rule. Below is an example of configuration.
# set interfaces map map0 rule 1 forwarding-mode encapsulation # set interfaces map map0 rule 1 forwarding-rule false
forwarding-mode を混在させることも可能です。たとえば Mapping Rule A と Mapping Rule B があった場合、 Mapping Rule A の forwarding-mode を translation とし、 Mapping Rule B の forwarding-mode を encapsulation とするような設定も可能です。その場合すべての BR/CE で Mapping Rule A の forwarding-mode を translation に、 Mapping Rule B の forwarding-mode を encapsulation にする必要があります。
You can set the both forwarding modes. If Mapping Rule A and Mapping Rule B exist, you can set the "translation" as a "forwarding-mode" on the Mapping Rule A, and the "encapsulation" as a "forwarding-mode" on the Mapping Rule B. In this case, you need to set the same "forwarding-mode" for Mapping Rule A (which is translation) and Mapping Rule B (which is encapsulation) on all of BRs/CEs.
forwarding-mode を混在させた場合、 destination address 側に match する Mapping Rule の forwarding-mode が適用されます。たとえば default-forwarding-mode が encapsulation で、 Mapping Rule の forwarding-mode がすべて translation の場合、 CE から BR 方向は encapsulation が適用され、 BR から CE 方向は translation が適用されます。
If both forwarding modes are set, "forwarding-mode" that match with the side of destination address is applied as a "forwarding-mode". For example, if the "default-forwarding-mode" is "encapsulation" and the all "forwarding-mode" is "translation" on the Mapping Rule, encapsulation is applied for the packets from CE to BR, and translation is applied the packets from BR to CE.
BR では forwarding-rule は必ず true にしてください。
"forwarding rule" needs to be "true" on the BR.
# set firewall send-redirects disable # set interfaces map map0 role br # set interfaces map map0 br-address 2001:db8::1/64 # set interfaces map map0 default-forwarding-mode translation # set interfaces map map0 default-forwarding-rule true # set interfaces map map0 rule 1 ipv6-prefix 2001:db8:89ab::/48 # set interfaces map map0 rule 1 ipv4-prefix 192.0.2.0/24 # set interfaces map map0 rule 1 ea-length 16 # set protocols static interface-route 192.0.2.0/24 next-hop-interface map0
*注意* BR アドレスである 2001:db8::1/64 をどこかのインターフェースに手動で設定したりしないでください。
NOTE: You must not set any interface address to 2001:db8::1/64(BR address) manually.
上記のように設定すると br-address で指定したプレフィクスを map0 仮想インターフェースに向ける静的ルーティングの設定が自動で入ります。
When the above configuration is set, the static route with next hop of map0 virtual interface is automatically set. This static route is for IPv6 prefix which is set as a br-address.
$ show ipv6 route
Codes: K - kernel route, C - connected, S - static, R - RIPng, O - OSPFv3,
I - ISIS, B - BGP, * - FIB route.
C>* ::1/128 is directly connected, lo
K>* 2001:db8::/64 is directly connected, map0
S>* 2001:db8:100::/40 [1/0] via 2001:db8:ffff:ffff::2, eth1
C>* 2001:db8:ffff:ffff::/64 is directly connected, eth1
C * fe80::/64 is directly connected, eth0
C>* fe80::/64 is directly connected, eth1
IPv6 ネットワーク内の他のルータでは 2001:db8::/64 をこの BR に向けるようルーティングする必要があります。
You need to set the IPv6 routing for 2001:db8::/64 toward BR on the routers in the IPv6 network.
# set firewall send-redirects disable # set interfaces ethernet eth1 address 2001:db8:89ab:cdef::1/64 # set interfaces ethernet eth1 address 192.168.1.1/24 # set interfaces map map0 role ce # set interfaces map map0 tunnel-source eth1 # set interfaces map map0 br-address 2001:db8::1/64 # set interfaces map map0 default-forwarding-mode translation # set interfaces map map0 default-forwarding-rule true # set interfaces map map0 rule 1 ipv6-prefix 2001:db8:89ab::/48 # set interfaces map map0 rule 1 ipv4-prefix 192.0.2.0/24 # set interfaces map map0 rule 1 ea-length 16 # set protocols static interface-route 0.0.0.0/0 next-hop-interface map0 # set policy route mssclamp rule 1 protocol tcp # set policy route mssclamp rule 1 tcp flags SYN # set policy route mssclamp rule 1 set tcp-mss 1200 # set interfaces ethernet eth1 policy route mssclamp # set system name-server 2001:db8:ffff:ffff::1 # set system name-server 2001:db8:ffff:ffff::2 # set service dhcp-server shared-network-name MY_NET subnet 192.168.1.0/24 start 192.168.1.100 stop 192.168.1.199 # set service dhcp-server shared-network-name MY_NET subnet 192.168.1.0/24 default-router 192.168.1.1 # set service dhcp-server shared-network-name MY_NET subnet 192.168.1.0/24 dns-server 192.168.1.1 # set service dns forwarding listen-on eth1
*注意* MAP IPv6 アドレスである 2001:db8:89ab:cdef:0:c000:2cd:ef/128 は静的ルーティングとして自動で設定されます。このアドレスをどこかのインターフェースに手動で設定たりしないでください。
NOTE: 2001:db8:89ab:cdef:0:c000:2cd:ef/128(MAP IPv6 address) will be configured as static route to MAP virtual interface by automatically. You must not set any interface address to this manually.
*注意* CE 側で利用する DNS キャッシュサーバは IPv6 のものを利用することを強く推奨します。
NOTE: It is strongly recommended to set IPv6 DNS server as the "system name-server" on the CE.
以下のような設定も可能です(デフォルトは 6)。
You can set the following command. (Default value of PSID offset is 6)
# set interfaces map map0 rule 1 psid-offset 4
PSID length が正の数以外の条件(draft-ietf-softwire-map の用語に従うと Complete IPv4 address のケースと IPv4 prefix のケース)でデフォルトで NAPT が有効です。これらの条件時に NAPT を殺したいときは以下の設定をします。
When PSID length is not positive value (According to in the draft-ietf-softwire-map terms, the case is Complete IPv4 address or IPv4 prefix) , NAPT is enabled by default. In this case, you can disable NAPT by the following command.
# set interfaces map map0 napt-always false
NAPT を殺した状態では MAP 仮想インターフェースに IPv4 アドレスを振り iptables による NAT を利用することができます。
When NAPT is disabled, you can use NAT on iptables by assigning IPv4 address on the MAP virtual interface.
# set interfaces map map0 address 192.0.2.205/32 # set nat source rule 1 outbound-interface map0 # set nat source rule 1 translation address masquerade # set nat destination rule 1 inbound-interface map0 # set nat destination rule 1 protocol tcp # set nat destination rule 1 destination port 80 # set nat destination rule 1 translation address 192.168.1.10
TCP のポート番号が枯渇した際にもっとも使用頻度の低い NAPT エントリーを強制的に再利用するように設定することができます(デフォルトは false)。
In case of TCP port number exhaustion, you can set the following command for enforced reusing less frequently used NAPT entries. (Default setting is false)
# set interfaces map map0 napt-force-recycle true
ポート番号強制再利用の機能は UDP と ICMP では無効化することはできません。
However, UDP and ICMP is unable to reuse port number.
実際に MAP を展開する際には全ての BR/CE の MTU の値を統一することが望ましいです。以下のコマンドを実行することで IPv6 パケットの最大サイズを設定することができます。以下の例では MAP により encapsulation/translation される IPv6 パケットのサイ>ズが最大で 1500 バイトとなるよう分割されます(デフォルトは 1280)。
When you deploy MAP in your network, you should set same MTU value on all of BRs/CEs. You can set the MTU value as below. The following command does the fragmentation to 1500 Byte for IPv6 packets toward encapsulation/translation. (Default value is 1280)
# set interfaces map map0 ipv6-fragment-size 1500
encapsulation の場合、デフォルトでは IPv6 ヘッダの直後にかならず IPv4 ヘッダが付くよう IPv4 スタックでフラグメント処理を行います。以下の設定をすることで IPv4 スタックではなく IPv6 スタックでフラグメントするよう設定を変更することができます。
In case that encapsulation is configured, the fragmentation process is performed in the IPv4 stack by default so that IPv4 packet header puts right behind IPv6 packet header. You can change the fragmentation handling from the IPv4 stack to the IPv6 stack by the following command.
# set interfaces map map0 ipv4-fragment-inner false
以下のように設定することで MAP 1:1 として利用することもできます。
You can configure MAP 1:1 as below.
# set interfaces map map0 rule 1 ipv6-prefix 2001:db8:1234::/48 # set interfaces map map0 rule 1 ipv4-prefix 192.0.2.18/32 # set interfaces map map0 rule 1 psid-prefix 0x34/8 # set interfaces map map0 rule 1 ea-length 0 # set interfaces map map0 rule 2 ipv6-prefix 2001:db8:5678::/48 # set interfaces map map0 rule 2 ipv4-prefix 192.0.2.18/32 # set interfaces map map0 rule 2 psid-prefix 0x56/8 # set interfaces map map0 rule 2 ea-length 0
上記の設定では 192.0.2.18/32 という 1 つの IPv4 アドレスを PSID が 0x34 の CE と PSID が 0x56 の CE の 2 台で共有することができます。PSID が 0x34 の CE の MAP IPv6 アドレスと PSID が 0x56 の CE の MAP IPv6 アドレスはそれぞれ 2001:db8:1234::c000:212:34 と 2001:db8:5678::c000:212:56 になります。
On the above configuration, an IPv4 address of 192.0.2.18/32 can be shared by the CE with 0x34 as a PSID and the other CE with 0x56. The CE with 0x34 has 2001:db8:1234::c000:212:34 as a MAP IPv6 address, and the other CE with 0x56 has 2001:db8:5678::c000:212:56.
以下のように設定することで 464XLAT CLAT として利用することができます。
You can set 464XLAT CLAT on this implementation by the following configuration.
# set interfaces ethernet eth1 address 2001:db8:89ab:cdef::1/64 # set interfaces ethernet eth1 address 192.168.1.1/24 # set interfaces map map0 role ce # set interfaces map map0 tunnel-source eth1 # set interfaces map map0 br-address 2001:db8::1/64 # set interfaces map map0 default-forwarding-mode translation # set protocols static interface-route 0.0.0.0/0 next-hop-interface map0
JPIX さんが実験的に提供されている IPv6v4 エクスチェンジサービス で動作検証を行っています。 JPIX さんの IPv6v4 エクスチェンジサービスを利用する場合は br-address の 2001:db8::1/64 の部分を JPIX さんが提供されている NAT64 のプレフィクス(****:****:****:****::/96)に置き換えてください。
This implementation was tested in IPv6v4 Exchange Service by JPIX. If you use this implementation in the JPIX service, you need to change "br-address" to NAT64 prefix (****:****:****:****::/96) provided by JPIX.
*注意* LAN 側プレフィクスのうち ****:****:****:****:0:6464:****:****/96 の部分(上記の例では 2001:db8:89ab:cdef:0:6464:****:****/96 の部分)は translation の為に使用されるため使用できなくなりますのでご注意ください。
NOTE: ****:****:****:****:0:6464:****:****/96 is unable to use as an IPv6 prefix for the LAN-side.
また MAP CE の設定と同様、フラグメントを回避するために TCP MSS の書き換え処理は必ず行います。以下の例では eth1 から出て行こうとする TCP SYN パケットの MSS の値を 1212 とするよう設定しています。以下の例のうち eth1 の部分は適宜 LAN 側のインターフェース名に置き換えてください。
As is the case for MAP CE, you need to set the TCP MSS clamping for avoiding fragmentation. In the following example, The value of MSS in the TCP SYN packet is set to 1212. If you set this configuration, the interface name ("eth1" in this example) might be needed to change.
# set policy route mssclamp rule 1 protocol tcp # set policy route mssclamp rule 1 tcp flags SYN # set policy route mssclamp rule 1 set tcp-mss 1212 # set interfaces ethernet eth1 policy route mssclamp
# set interfaces ethernet eth1 address 2001:db8:89ab:cdef::1/64 # set interfaces ethernet eth1 address 192.168.1.1/24 # set interfaces map map0 role ce # set interfaces map map0 tunnel-source eth1 # set interfaces map map0 br-address 2001:db8::1/64 # set interfaces map map0 default-forwarding-mode encapsulation # set protocols static interface-route 0.0.0.0/0 next-hop-interface map0
# set policy route mssclamp rule 1 protocol tcp # set policy route mssclamp rule 1 tcp flags SYN # set policy route mssclamp rule 1 set tcp-mss 1200 # set interfaces ethernet eth1 policy route mssclamp
# set interfaces map map0 role br # set interfaces map map0 br-address 2001:db8::1/64 # set interfaces map map0 default-forwarding-mode translation # set interfaces map map0 pool 1 pool-prefix 203.0.113.123/32 # set protocols static interface-route 203.0.113.123/32 next-hop-interface map0
# set interfaces map map0 role br # set interfaces map map0 br-address 2001:db8::1/64 # set interfaces map map0 default-forwarding-mode encapsulation # set interfaces map map0 pool 1 pool-prefix 203.0.113.123/32 # set protocols static interface-route 203.0.113.123/32 next-hop-interface map0
現在の MAP 仮想インターフェースの設定を確認したいときは以下のコマンドを実行します。
Use the following command to display the current configuration for MAP virtual interface.
$ show interfaces map map0
Interface name : map0
Role : CE
Tunnel source : eth1
BR address : 2001:db8::1/96
IPv4 pool :
Default forwarding mode : translation
Default forwarding rule : true
IPv6 fragment size : 1500
IPv4 fragment inner : true
NAPT always : true
NAPT force recycle : false
Basic mapping rule :
Rule IPv6 prefix : 2001:db8:100::/40
Rule IPv4 prefix : 172.16.1.0/32
Rule PSID prefix : 0x88/8
EA-bits length : 0
PSID offset : 6
Forwarding mode : translation
Forwarding rule : true
MAP IPv6 address : 2001:db8:100::ac10:100:88/128
Shared IPv4 address : 172.16.1.0
Assigned port-set ID : 0x88/8
Port-set :
Port-set #0000 : 1568(0x0620) - 1571(0x0623)
Port-set #0001 : 2592(0x0a20) - 2595(0x0a23)
Port-set #0002 : 3616(0x0e20) - 3619(0x0e23)
...長いので途中省略...
Port-set #0062 : 65056(0xfe20) - 65059(0xfe23)
現在設定されている MAP Rule の一覧を確認したいときは以下のコマンドを実行します。
The following command is for displaying the current MAP rule.
$ show interfaces map map0 rule
Mode: 'E' = Encapsulation, 'T' = Translation. FMR: 'T' = FMR, '-' = Not FMR.
IPv6 prefix, IPv4 prefix, PSID prefix, EA-bits length, PSID offset, Mode, FMR.
0: 2001:db8:100::/40 172.16.1.0/32 0x0088/8 0 6 T F
現在の NAPT のセッション・テーブルを確認したいときは以下のコマンドを実行します。
The following command is for displaying the current NAPT session table.
$ show interfaces map map0 napt
Proto: 'I' = ICMP, 'T' = TCP, 'U' = UDP.
Flags: SynOut, SynAckIn, AckOut, FinOut, FinAckIn, FinIn, FinAckOut, Rst.
'!' = Up, '.' = Down.
Last used, Local address:port, Mapped port, Remote address:port, Proto, Flags.
09:34:38 192.168.11.11:3129 32288(0x7e20) 10.1.1.11:0 I ........
464XLAT PLAT か DS-Lite AFTR として動作させているときは以下のように表示されます。
The following shows a result in the case of 464XLAT PLAT or DS-Lite AFTR.
$ show interfaces map map0 napt
Proto: 'I' = ICMP, 'T' = TCP, 'U' = UDP.
Flags: SynOut, SynAckIn, AckOut, FinOut, FinAckIn, FinIn, FinAckOut, Rst.
'!' = Up, '.' = Down.
Last used, Local IPv6 address, Local address:port, Mapped address:port, Remote address:port, Proto, Flags.
09:31:43 2001:db8:112:3400:c0:0:200:0 192.168.11.11:3129 172.16.2.0:(0x84d9)34009 10.1.1.11:0 I ........
実装にあたりソフトバンクテレコムの松嶋さんにいろいろと教えていただきました。その上 ASAMAP という素敵な名前までつけて頂いちゃいました。ありがとうございます!!!
Thanks Matsushima-san from Softbank Telecom for lots of advices and giving nice name "ASAMAP" to this implementation.
JPIX の馬渡さんにこの文書の英訳をしていただきました。ありがとうございます!!!めちゃくちゃ嬉しいです!!!
Thanks Mawatari-san from JPIX for English translation of this document. I'm insanely happy! (I was translated into English this sentence only ;) ).
あ、もちろん実装上の問題は浅間の問題ですので為念。もしなにかございましたら Twitter で @m_asama にメンションでも飛ばしていただければ幸いです。もしかしたらなんとかするかも。
If you have any questions or notice any problems, those are due to Asama's issues. In that case, please feel free to contact @m_asama by twitter. Something might be done.